food protein induced enterocolitis syndrome treatment
As they have more milk protein and a lower. We review here the peculiar.
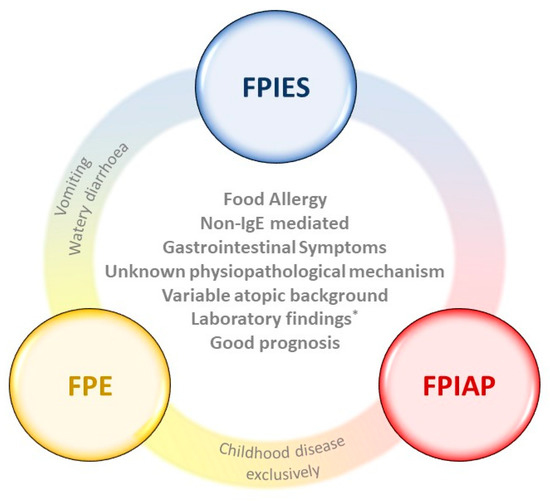
Foods Free Full Text Non Ige Mediated Gastrointestinal Food Protein Induced Allergic Disorders Clinical Perspectives And Analytical Approaches Html
Avoidance of triggering foods ensuring good nutrition healing the gut balancing the immune system and.

. Food Protein-Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome FPIES is an inflammation involving both the small intestine and the large intestine colon. Food Protein-Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome. FPIES usually develops in infancy and resolves around 3-5 years of age.
Food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES is a non-IgE-mediated food allergy that has been well-characterized clinically yet it is still poorly understood. Like other food allergies. Food Protein-Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome FPIES sometimes referred to as a delayed food allergy is a severe condition causing vomiting and diarrhea.
Treatment of food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome. Usual symptoms include vomiting diarrhoea. Food Protein-Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome FPIES is a rare disorder mostly affecting infants 0-3 years and young children 3-10 years which occurs when foods that harm.
In the last years the interest of the scientific community toward food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES has grown exponentially. Food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES is a non-IgE-mediated gastrointestinal food hypersensitivity usually triggered by cows milk or soy protein. 20 mlkg boluses of isotonic saline.
Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome FPIES is a type of non-IgE mediated food allergy that can present with severe vomiting diarrhea and dehydration. Food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES is a non-IgE-mediated food allergy that manifests with projectile repetitive emesis that can be followed by diarrhea and. Food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome is still a mysterious disease pathogenically poorly characterized although the first FPIES case has been described in 1967.
Intravenous fluids if dehydrated. Intravenous fluids if moderate to severe. Food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES is a delayed non-IgE mediated gut allergic reaction to a foods usually presenting in the first two years of life with an estimated.
Food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES is a non-IgE-mediated gastrointestinal food allergic disorder that has gained a major interest the past decade. Removal of causative food from diet. Food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES Food protein-induced allergic proctocolitis FPIAP Food protein-induced enteropathy FPE.
Prevention and Management The only way to prevent a Food Protein-Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome FPIES reaction is to strictly avoid the culprit food in the diet. Symptoms include severe vomiting and diarrhea and. Food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES is a non IgE-mediated gastrointestinal food allergy that presents with delayed vomiting after ingestion primarily in.
Classic symptoms of FPIES include profound vomiting. Diarrhea that begins after vomiting. About Food Protein-Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome American Academy of Allergy Asthma and Immunology.
Food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES is an uncommon disorder characterized by an allergic reaction to food that affects the gastrointestinal system. Food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES is an uncommon and potentially severe non-IgE-mediated food allergy. FPIES food protein induced enterocolitis syndrome is a serious allergic reaction to certain foods.
Acute FPIES is characterized. Oral rehydration fluids if mild. Symptoms of food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome can vary from child to child and in severity.
Food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES is a severe presentation of non-IgE-mediated food allergy affecting the gastrointestinal GI tract mainly in. If a severe reaction does occur. Food Protein-Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome FPIES is a type of food allergy affecting the gastrointestinal GI tract.
Vomiting typically occurring two hours after ingestion.

Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome The Journal Of Allergy And Clinical Immunology In Practice

Oral Food Challenge In Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome Download Table

Pdf Gastrointestinal Food Allergy In Infants Semantic Scholar
Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome Fpies And Nutrition

Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome Oral Food Challenge Annals Of Allergy Asthma Immunology

Dietary Management Of Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome During The Coronavirus Disease 2019 Pandemic Annals Of Allergy Asthma Immunology

Interpretation Of The Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome Oral Download Table
Two Case Reports Of Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis

Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome Fpies Treatment Allergy Cure

Clinical Types Of Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome Fpies Download Scientific Diagram

Fpies Action Plan Australasian Society Of Clinical Immunology And Allergy Ascia

Managing Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome During The Coronavirus Disease 2019 Pandemic Annals Of Allergy Asthma Immunology
Fpies Treatment Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome Dr Green Mom

Management Of Acute Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome Emergencies At Home And In A Medical Facility Annals Of Allergy Asthma Immunology

Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome Annals Of Allergy Asthma Immunology
Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome As A Cause For Infant Hypotension The Western Journal Of Emergency Medicine
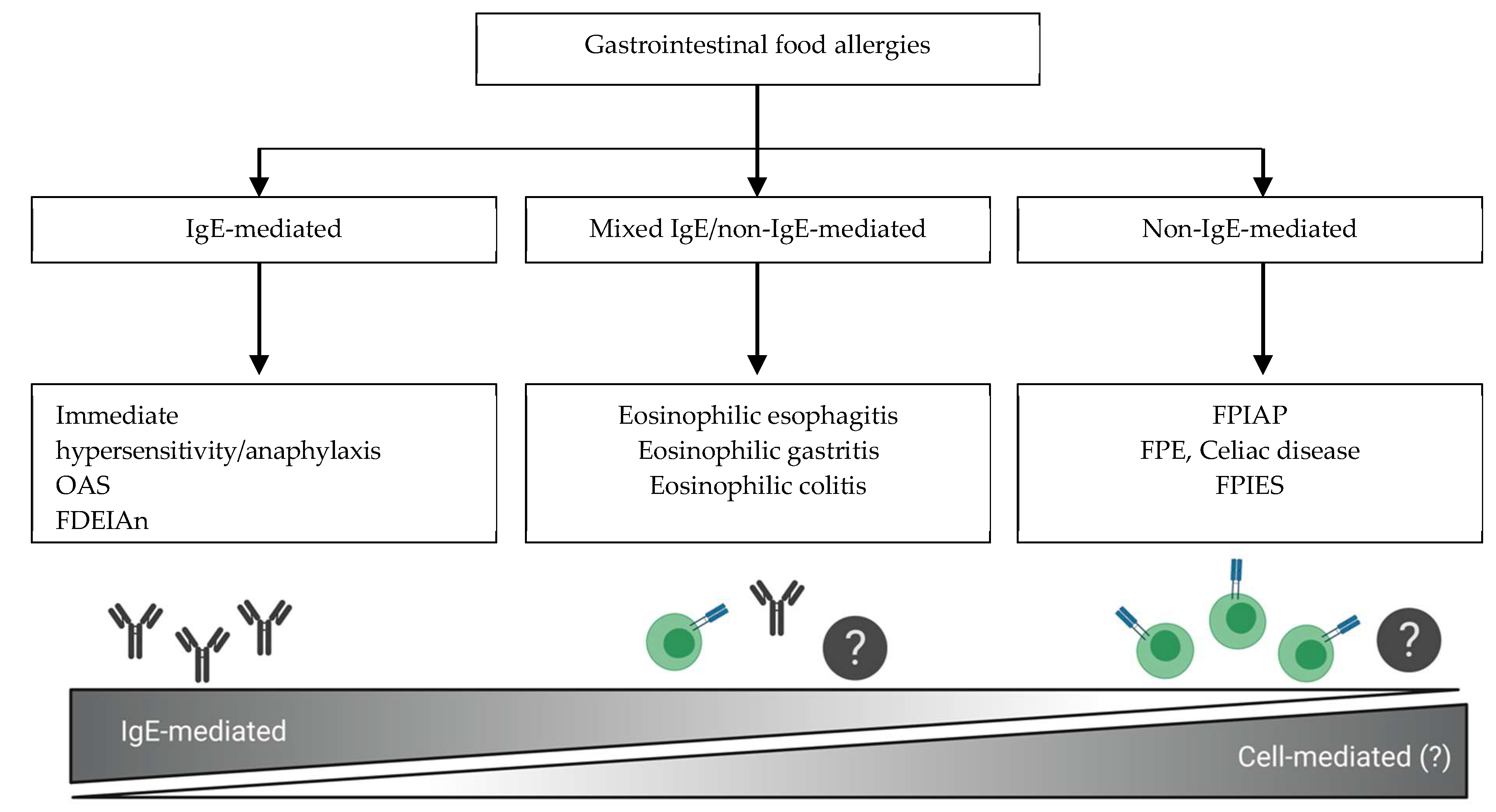
Nutrients Free Full Text Non Ige Mediated Gastrointestinal Food Allergies In Children An Update Html

Clinical Types Of Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome Fpies Download Scientific Diagram